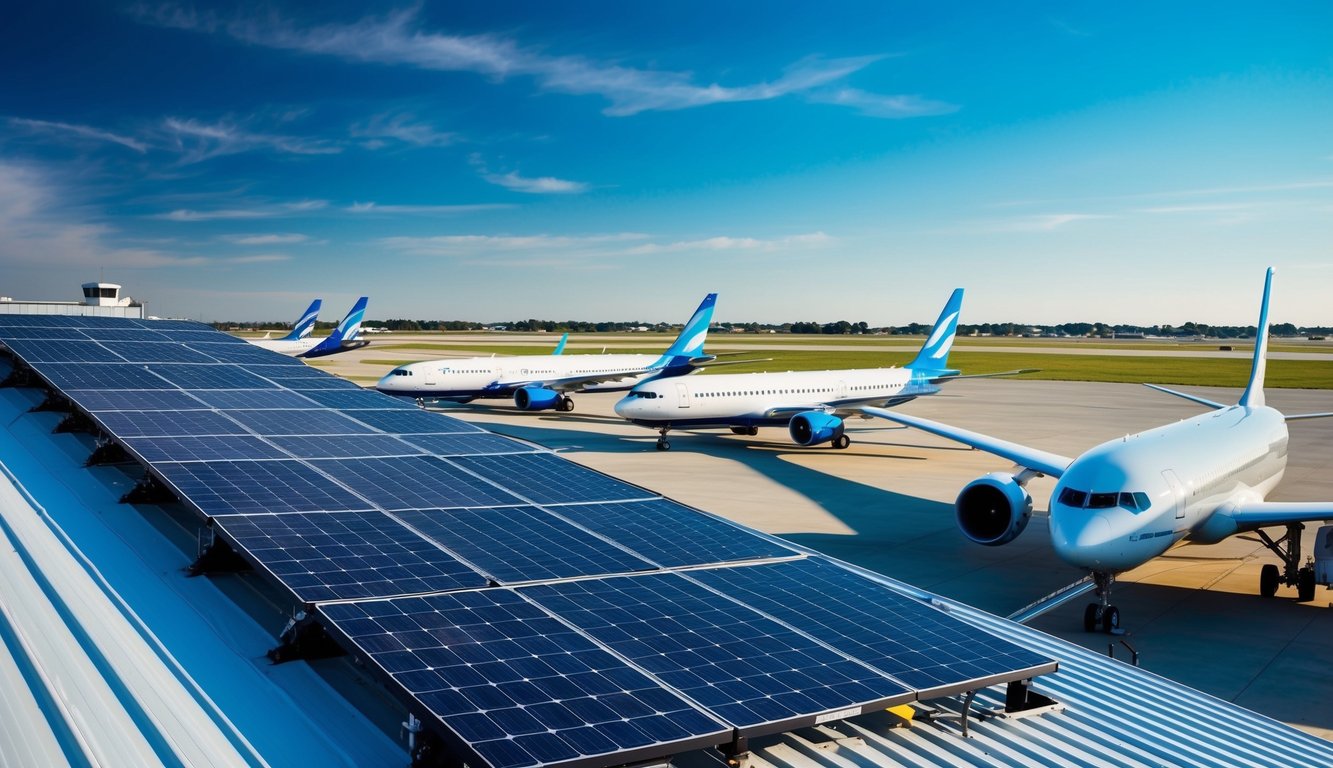
Solar Panel for Airports: Powering Sustainable Air Travel
Solar panels for airports offer a sustainable energy solution that can significantly reduce operational costs and environmental impact. Airports worldwide are increasingly adopting solar power to meet their energy needs and reduce carbon emissions. These installations range from small rooftop arrays to large ground-mounted systems, generating clean electricity to power various airport facilities.
Integrating solar panels into airport infrastructure presents unique challenges and opportunities. Panels must be carefully positioned to avoid glare that could interfere with aircraft operations or air traffic control. Despite these considerations, many airports have successfully implemented solar projects, demonstrating their viability and benefits.
The use of solar power in airports aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and promote renewable energy. As technology advances and costs decrease, more airports are likely to embrace solar energy as a key component of their sustainability strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Solar panels can significantly reduce airport operational costs and carbon emissions
- Careful planning is required to integrate solar installations without affecting aviation safety
- Airports worldwide are increasingly adopting solar power as part of their sustainability efforts
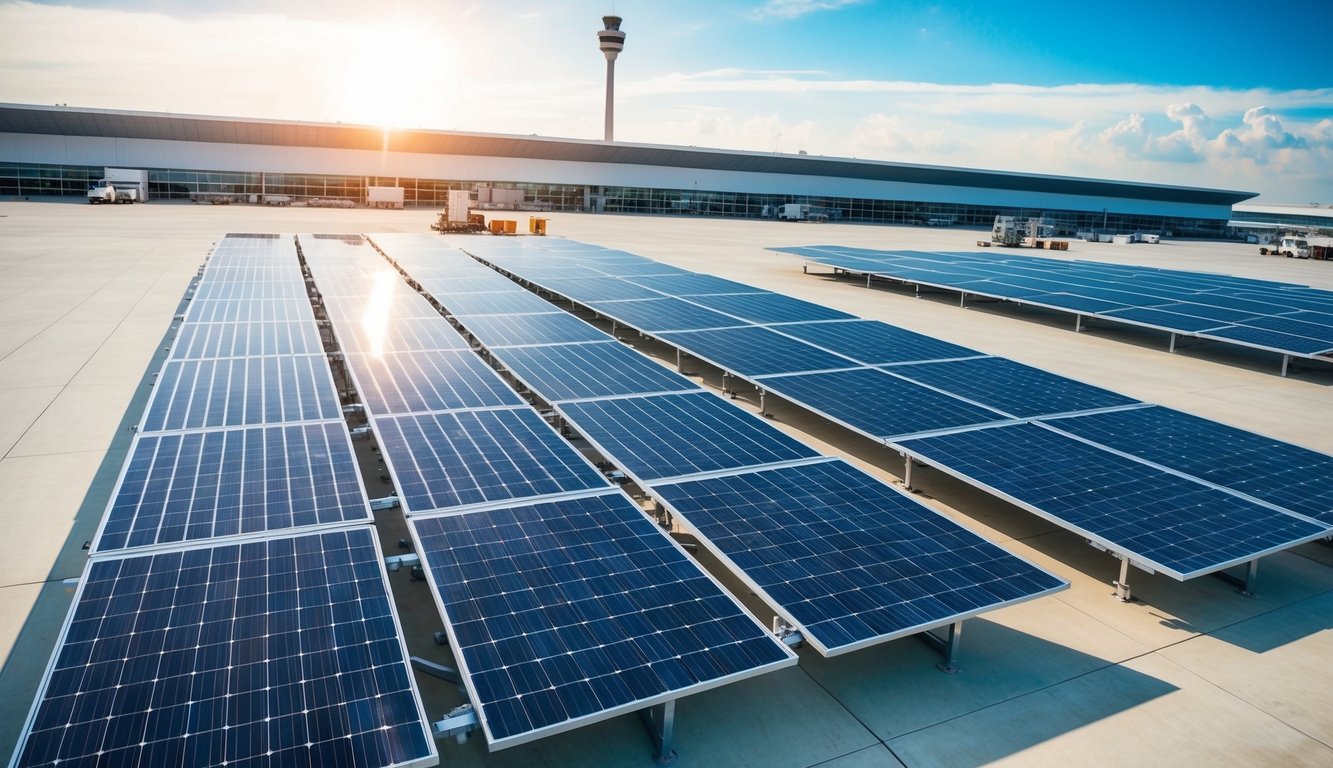

Understanding Solar Panels In Airport Infrastructure
Solar panels offer airports a sustainable energy solution, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. These systems harness sunlight to generate electricity, supporting various airport functions.
Types of Solar Panels Suitable for Airports
Monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels are commonly used in airport settings. Monocrystalline panels, made from single-crystal silicon, boast higher efficiency and a sleek appearance. Polycrystalline panels, whilst slightly less efficient, are more cost-effective.
Thin-film panels are another option, ideal for curved surfaces or areas with limited load-bearing capacity. These flexible panels can be integrated into building materials, making them suitable for airport roofs and facades.
Bifacial panels, which capture light from both sides, are gaining popularity. They can increase energy yield by up to 30%, making them particularly useful in open airport spaces.
Space Requirements and Installation Considerations
Airports typically have vast open areas, making them ideal for large-scale solar installations. Ground-mounted systems are common, utilising otherwise unused land near runways or in buffer zones.
| Installation Type | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Ground-mounted | Large-scale potential, easy maintenance | Land use, potential glare |
| Rooftop | Utilises existing structures, minimal land use | Structural load, roof condition |
| Carport | Dual-purpose (energy + shade), visible sustainability | Initial cost, parking layout |
Glare assessment is crucial to ensure solar panels don’t interfere with pilot or air traffic controller vision. Proper positioning and anti-glare coatings can mitigate these risks.
Integration with Existing Airport Systems
Solar panels can be seamlessly integrated with airports’ electrical systems. Inverters convert the DC power from panels to AC power used by airport facilities. Smart grid technologies enable efficient energy distribution and storage.
Battery storage systems allow airports to use solar energy during peak demand or cloudy periods. This enhances energy reliability and reduces dependence on the main grid.
Solar power can support various airport operations, including:
- Terminal lighting and air conditioning
- Runway and taxiway lighting
- Electric vehicle charging stations
- Baggage handling systems
Monitoring software helps track energy production and consumption, allowing airports to optimise their solar systems and demonstrate sustainability commitments to stakeholders.
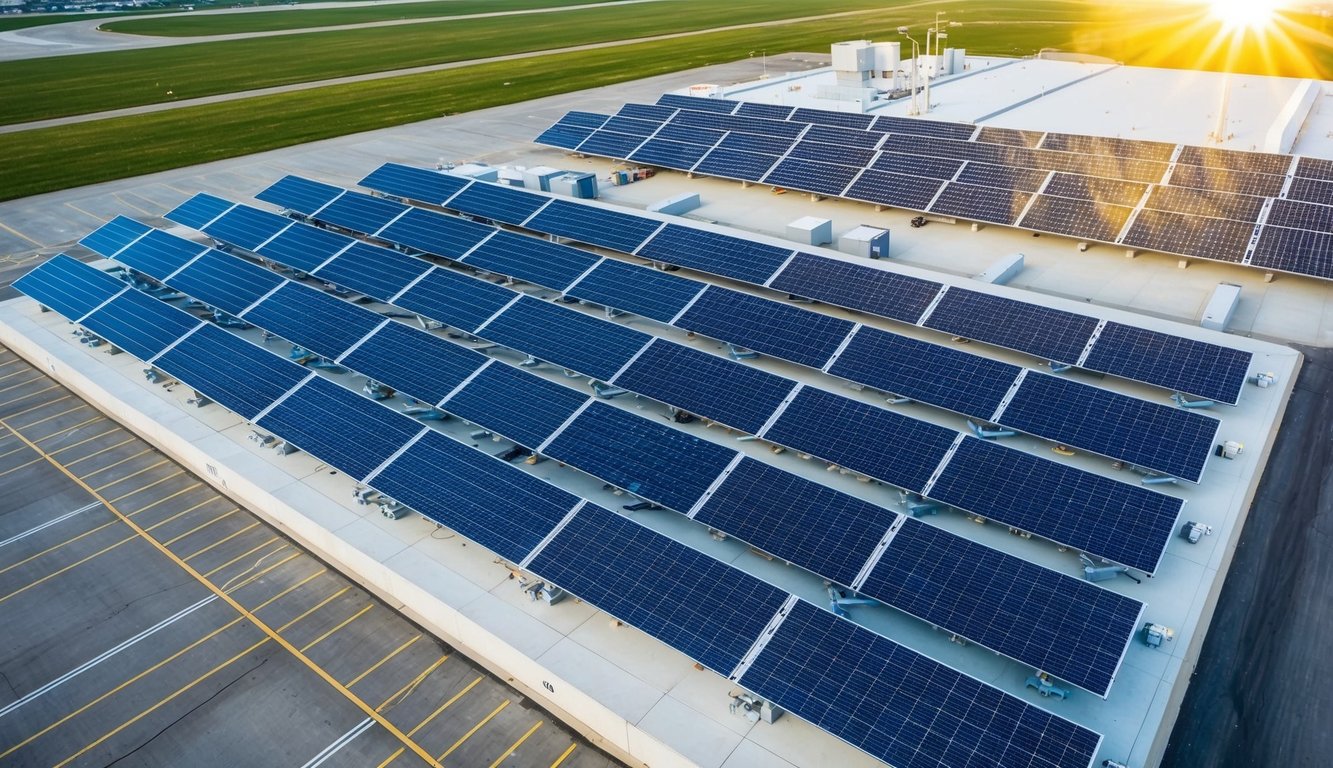

Benefits of Solar Panels at Airports
Solar panels offer airports substantial advantages in cost reduction, environmental sustainability, energy independence, and regulatory compliance. These systems provide multifaceted benefits that align with the goals of modern aviation facilities.
Energy Cost Reduction
Solar panels significantly reduce airports’ electricity expenses. By generating their own power, airports can lower reliance on costly grid electricity. Large-scale solar installations often produce surplus energy, allowing airports to sell excess power back to the grid for additional revenue.
Airports typically have vast unused spaces like rooftops and car parks, ideal for solar panel placement without extra land costs. This efficient use of existing infrastructure maximises return on investment.
Over time, solar systems offer predictable energy costs, shielding airports from volatile electricity prices. This financial stability aids long-term budgeting and resource allocation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Solar panels dramatically decrease airports’ carbon footprints. By replacing fossil fuel-derived electricity with clean solar energy, airports significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
This shift towards renewable energy enhances airports’ environmental profiles, appealing to eco-conscious travellers and airlines. It also helps meet increasingly stringent sustainability targets set by aviation authorities and governments.
Solar installations often serve as visible symbols of an airport’s commitment to sustainability. This can improve public perception and strengthen relationships with local communities concerned about air quality and noise pollution.
Energy Independence and Security
Solar panels bolster airports’ energy security by diversifying power sources. This reduces vulnerability to grid outages or supply disruptions, which could otherwise impact critical operations.
On-site solar generation provides a measure of energy autonomy, lessening dependence on external suppliers. This self-sufficiency is particularly valuable for airports in remote locations or areas with unreliable grid power.
During emergencies or natural disasters, solar-powered systems can maintain essential functions, enhancing an airport’s resilience and operational continuity.
Federal Aviation Administration Compliance
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has established guidelines for solar panel installation at airports, ensuring compatibility with aviation safety. Properly designed solar systems comply with these regulations while delivering energy benefits.
FAA-compliant solar panels use non-reflective materials to prevent glare that could distract pilots. Careful placement avoids interference with radar systems and flight paths.
Meeting FAA standards for solar installations demonstrates an airport’s commitment to safety alongside sustainability. This proactive approach can streamline approval processes for future expansion or modernisation projects.
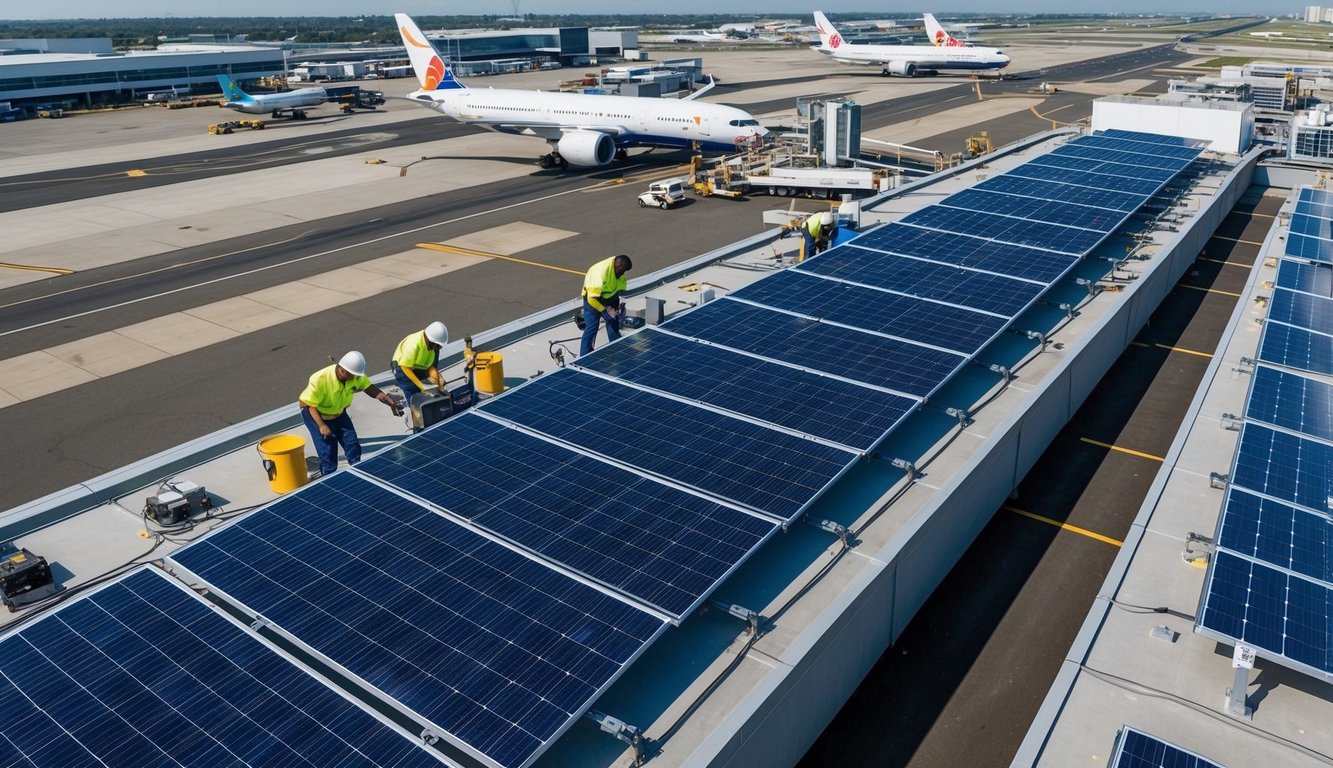

Key Implementation Challenges
Airports face several hurdles when integrating solar panel systems into their infrastructure. These challenges require careful planning and strategic solutions to ensure successful implementation.
Aircraft Glare Considerations
Glare from solar panels poses a significant concern for aircraft safety. Reflections can potentially distract pilots during critical flight phases. Glare Analysis Tools play a crucial role in mitigating this issue. These tools help assess and predict potential glare impacts on air traffic control towers and flight paths.
Proper panel placement and tilt angles are essential to minimise glare risks. Anti-reflective coatings on solar panels can further reduce reflectivity. Regular monitoring and adjustments may be necessary to maintain optimal panel orientation throughout the year.
Airports must work closely with aviation authorities to ensure compliance with glare-related regulations. This collaboration often involves conducting thorough glare studies and obtaining necessary approvals before installation.
Weather and Climate Factors
Local weather patterns and climate conditions significantly impact solar panel performance at airports. Extreme temperatures, heavy snowfall, and high winds can affect energy output and system durability.
In regions with frequent storms, panels must withstand strong gusts and potential debris impact. Robust mounting systems and high-quality materials are crucial for longevity. Snow accumulation on panels can reduce efficiency, necessitating effective snow removal strategies.
Airports in hot climates may face reduced panel efficiency due to overheating. Proper ventilation and cooling systems can help maintain optimal performance. Regular cleaning is essential to remove dust and sand buildup, which can diminish energy production.
Climate change considerations should also factor into long-term planning for airport solar installations.
Security and Safety Protocols
Integrating solar panels into airport infrastructure requires stringent security measures. Panels must not interfere with existing safety systems or create new vulnerabilities.
Access to solar array areas should be strictly controlled to prevent unauthorised entry. This may involve installing additional fencing, surveillance cameras, and alarm systems. Regular security audits are necessary to identify and address potential weaknesses.
Electromagnetic interference from solar equipment could potentially disrupt airport communication systems. Thorough testing and shielding measures are essential to prevent such issues.
Fire safety is another critical concern. Specialised fire suppression systems may be needed for solar installations, and emergency response teams should receive specific training for solar-related incidents.
Maintenance Requirements
Proper maintenance is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of airport solar installations. Regular inspections are necessary to identify and address issues promptly.
Panel cleaning schedules must be carefully coordinated to avoid disrupting airport operations. This may involve using specialised cleaning equipment or conducting maintenance during off-peak hours.
Electrical components, such as inverters and wiring, require periodic checks and replacements. Airports must ensure they have access to qualified technicians for both routine maintenance and emergency repairs.
Data monitoring systems play a vital role in tracking system performance and identifying potential issues. These systems should be integrated with existing airport management software for seamless operation.
Airports must also plan for panel degradation over time and budget for eventual replacements to maintain optimal energy production.
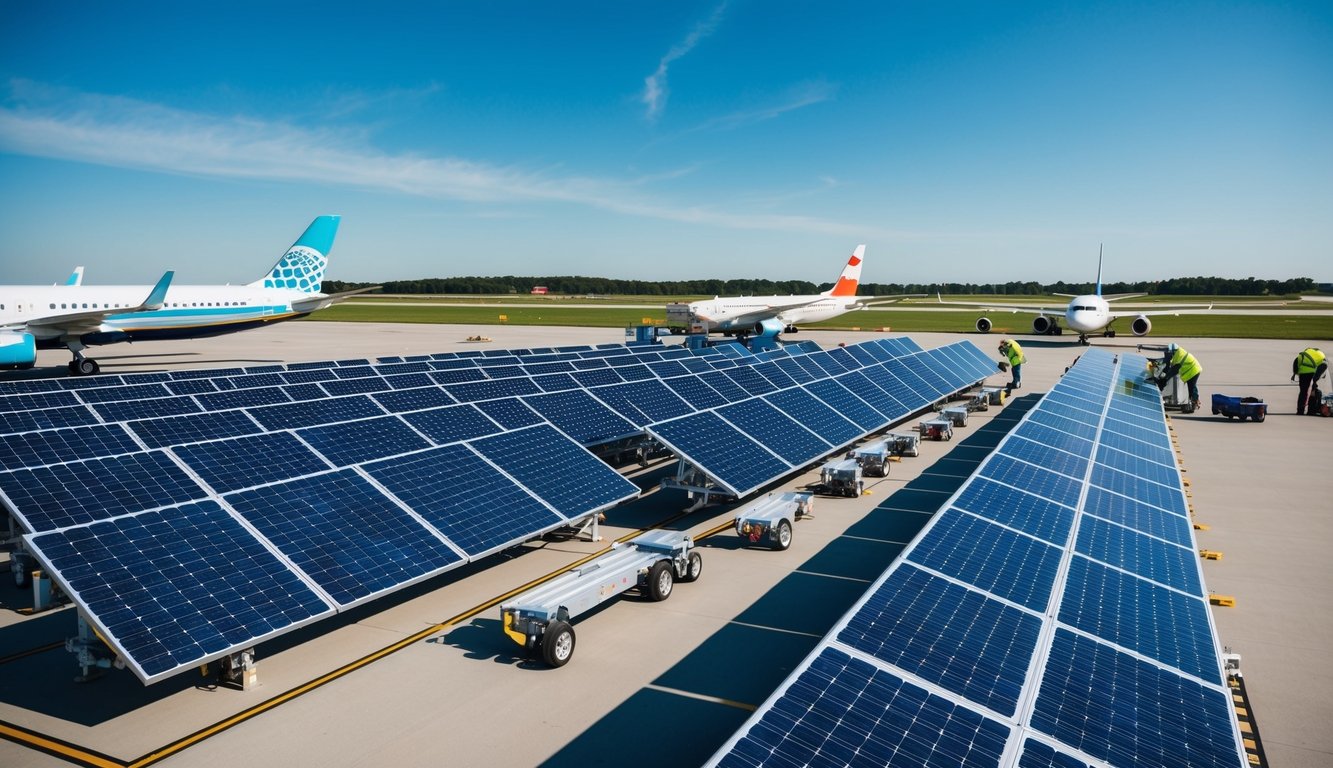

Best Practices for Airport Solar Installation
Implementing solar panels at airports requires careful planning and execution to ensure safety, efficiency, and optimal performance. Proper site assessment, equipment selection, installation guidelines, and monitoring systems are crucial for successful airport solar projects.
Site Assessment and Planning
A thorough site assessment is vital for airport solar installations. Consider available space, sun exposure, and potential glare issues. Evaluate rooftops, car parks, and open land areas for panel placement. Assess local climate conditions, including wind patterns and snow loads.
Engage with airport authorities early to address safety concerns and obtain necessary approvals. Review Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) guidelines for solar installations near runways and taxiways. Conduct glare studies using tools like the Solar Glare Hazard Analysis Tool to mitigate risks to pilots and air traffic control.
Analyse the airport’s energy consumption patterns to determine optimal system size. Consider future expansion plans and potential obstructions to solar access.
Equipment Selection Criteria
Choose high-quality, durable solar panels suited for airport environments. Select panels with anti-reflective coatings to minimise glare. Opt for robust mounting systems designed to withstand high winds and extreme weather conditions.
Consider bifacial panels to maximise energy production in areas with reflective surfaces. Choose inverters with advanced monitoring capabilities and remote shutdown features for enhanced safety.
Select equipment with proven track records in airport installations. Ensure compatibility with existing electrical infrastructure and compliance with local building codes.
Construction and Installation Guidelines
Prioritise safety during construction. Coordinate closely with airport operations to minimise disruptions to air traffic. Implement strict security protocols for construction personnel working in sensitive areas.
Use low-impact installation methods to protect airport surfaces. Employ ballasted mounting systems on rooftops to avoid penetrations. For ground-mounted systems, minimise excavation and use pre-cast concrete foundations where possible.
Install anti-glare fencing or vegetation buffers to mitigate potential glare impacts. Implement proper cable management to prevent interference with airport communication systems.
Conduct regular inspections during installation to ensure compliance with design specifications and safety standards.
Monitoring Systems Integration
Implement robust monitoring systems to track solar array performance and detect faults quickly. Integrate solar monitoring with the airport’s building management system for centralised control.
Install weather stations to correlate environmental conditions with system output. Utilise advanced data analytics to optimise energy production and identify maintenance needs.
Implement cybersecurity measures to protect solar monitoring systems from potential threats. Train airport staff on monitoring procedures and establish clear protocols for system alerts and maintenance responses.
Set up automated reporting to track energy savings and carbon emissions reductions. Use monitoring data to inform future solar expansion plans at the airport.
Case Studies of Successful Airport Solar Projects
Several airports worldwide have implemented solar panel installations, demonstrating the viability and benefits of renewable energy in aviation infrastructure. These projects showcase innovative approaches to sustainability and energy efficiency.
Denver International Airport
Denver International Airport (DIA) has embraced solar energy with multiple installations. The airport’s solar arrays, covering over 56 acres, generate approximately 10 megawatts of power. DIA’s commitment to renewable energy began in 2008 with its first solar installation.
The airport’s solar projects include:
- Solar array 1: 2 MW capacity, installed in 2008
- Solar array 2: 1.6 MW capacity, added in 2009
- Solar array 3: 4.4 MW capacity, completed in 2011
- Solar array 4: 2 MW capacity, operational since 2014
These solar installations help DIA reduce its carbon footprint and lower energy costs. The airport’s renewable energy initiatives have positioned it as a leader in sustainable airport operations.
Cochin International Airport
Cochin International Airport in Kerala, India, achieved a remarkable feat by becoming the world’s first fully solar-powered airport in 2015. The airport’s solar project consists of a 12 MWp solar power plant spread across 45 acres.
Key features of Cochin’s solar project:
- Power generation: Produces 50,000 to 60,000 units of electricity daily
- Carbon offset: Equivalent to planting 3 million trees
- Cost savings: Approximately £5.3 million over 25 years
The success of this project has inspired other airports in India to adopt solar power. Cochin International Airport serves as a model for sustainable airport operations globally.
Athens International Airport
Athens International Airport has implemented a significant solar power project as part of its commitment to sustainability. The airport’s photovoltaic park, launched in 2011, covers an area of 160,000 square metres.
Notable aspects of the Athens airport solar project:
- Capacity: 8 MWp, producing over 11 million kWh annually
- CO2 reduction: Approximately 10,000 tonnes per year
- Energy contribution: Meets 12.5% of the airport’s electricity needs
The solar park has helped Athens International Airport reduce its carbon footprint and energy costs while showcasing its dedication to environmental responsibility.
Indianapolis International Airport
Indianapolis International Airport boasts one of the largest airport-based solar farms in the world. The project, initiated in 2013, has expanded over the years to cover a substantial area of airport land.
Key features of Indianapolis airport’s solar installation:
- Total capacity: 20 MW across multiple phases
- Land utilisation: Covers 183 acres of previously unused land
- Power generation: Produces enough energy to power over 3,200 homes
The solar farm not only generates clean energy but also provides a significant source of non-aviation revenue for the airport. This project demonstrates how airports can effectively utilise vacant land for renewable energy production.
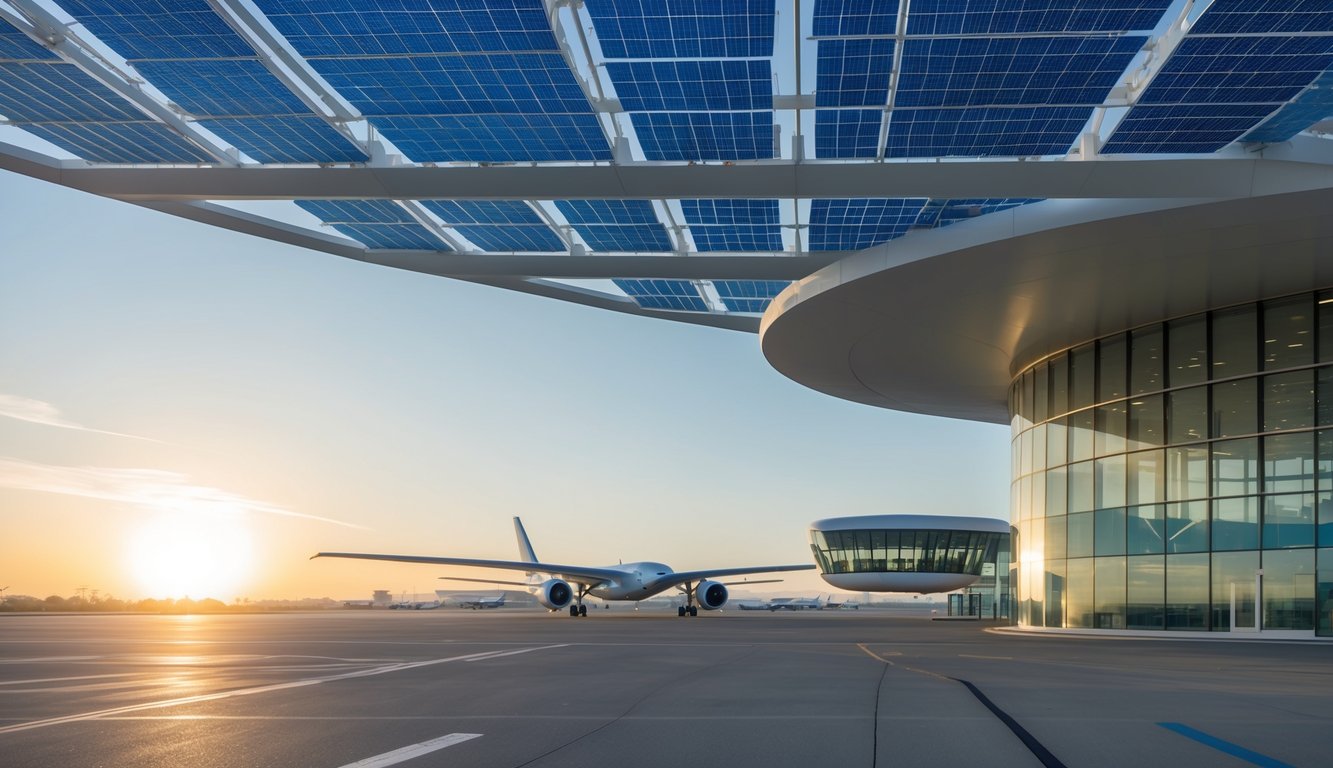

Future Trends in Airport Solar Technology
Solar technology at airports is rapidly evolving, with innovations promising increased efficiency and sustainability. New developments are set to transform how airports generate and manage renewable energy.
Emerging Solar Technologies
Perovskite solar cells are poised to revolutionise airport solar installations. These cells offer higher efficiency and lower production costs compared to traditional silicon panels. Thin-film solar technologies are also advancing, allowing for flexible and lightweight panels that can be integrated into airport structures more easily.
Bifacial solar panels, which capture sunlight from both sides, are gaining traction. These panels can boost energy production by up to 30% when installed on reflective surfaces like concrete or metal roofing.
Transparent solar cells are another exciting development. These could be used in airport windows and skylights, generating power without obstructing views or natural light.
Smart Grid Integration
Airports are increasingly adopting smart grid technologies to optimise solar energy use. Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) allows for real-time monitoring and management of energy flows. This enables airports to balance supply and demand more effectively.
Demand response systems are being implemented to adjust energy consumption based on grid conditions. During peak hours, non-essential systems can be automatically powered down to reduce strain on the grid.
Microgrids are becoming more common at airports. These localised power systems can operate independently from the main grid, enhancing resilience and allowing airports to maximise the use of their solar resources.
Energy Storage Solutions
Battery technology is advancing rapidly, with lithium-ion batteries becoming more efficient and affordable. Large-scale battery systems allow airports to store excess solar energy for use during cloudy days or at night.
Flow batteries are emerging as a promising option for long-duration energy storage. These systems can store large amounts of energy for extended periods, making them ideal for airport applications.
Hydrogen storage is also being explored. Excess solar energy can be used to produce hydrogen through electrolysis, which can then be stored and used in fuel cells to generate electricity when needed.
Expansion Possibilities
Airports are exploring innovative ways to expand their solar capacity. Floating solar arrays on airport retention ponds and reservoirs offer a space-efficient solution for increasing renewable energy production.
Agrivoltaics, the practice of combining solar panels with agriculture, could allow airports to utilise surrounding land for both energy generation and food production.
Vertical solar panels are being considered for installation along runway edges and other unused vertical surfaces, maximising land use efficiency.
Some airports are partnering with nearby communities to develop shared solar projects, extending the benefits of renewable energy beyond the airport boundaries.
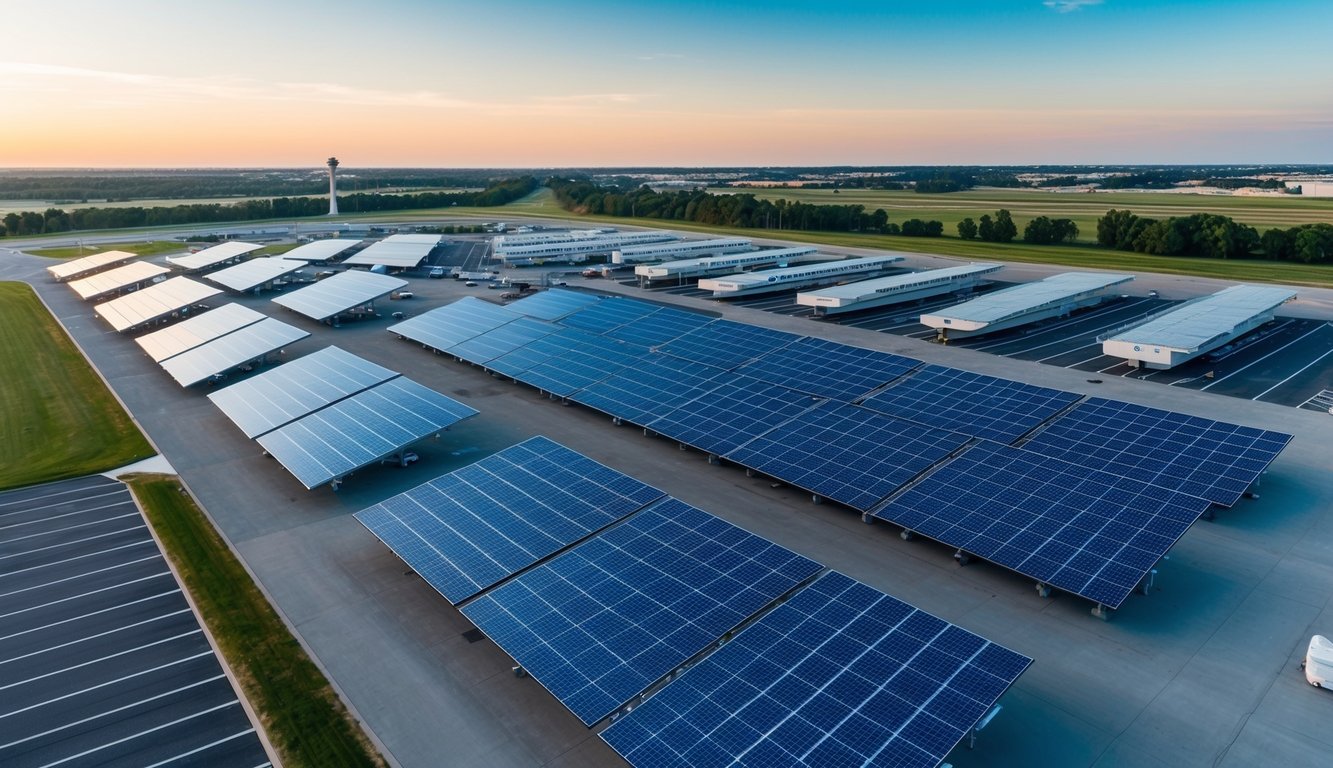

Conclusion
Solar panels for airports represent a pivotal advancement in sustainable aviation. You can see the tangible benefits these installations bring to airfields worldwide. They offer a reliable source of clean energy, significantly reducing carbon footprints and operational costs.
Airports adopting solar power demonstrate environmental leadership. You’ll find these systems seamlessly integrated into existing infrastructure, from rooftop arrays to ground-mounted panels near runways. The extensive open spaces at airports provide ideal conditions for large-scale solar farms.
The long-term cost savings are substantial. While initial investments may be significant, the reduced energy bills and low maintenance requirements quickly offset these expenses. Solar panels have impressive longevity, ensuring continued benefits for decades.
Here’s a snapshot of key advantages:
• Emission reduction: Cuts greenhouse gas output
• Energy security: Decreases reliance on grid power
• Public image: Enhances reputation as a green facility
• Adaptability: Tailored to specific airport needs
Embracing solar power at airports is not just a trend; it’s a necessary step towards a greener future in aviation. You’re witnessing a transformation that aligns air travel with sustainable practices, setting a positive example for other industries to follow.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solar panels at airports offer promising renewable energy solutions, but they come with unique considerations. Let’s explore some common queries about implementing solar power at aviation facilities.
What factors should be considered when selecting solar panels for airport installations?
When choosing solar panels for airports, you must prioritise safety and efficiency. Consider low-reflectivity panels with anti-glare coatings to minimise potential impacts on pilots and air traffic control. Panel height and placement should comply with obstacle limitation surfaces to avoid interfering with flight operations. Durability against weather extremes and wildlife resistance are also crucial factors.
How much does it generally cost to install solar panels at an airport?
The cost of installing solar panels at airports varies widely based on scale, location, and specific requirements. Typically, large-scale airport solar projects can range from £1 million to £10 million or more. Factors affecting cost include panel type, mounting systems, electrical infrastructure upgrades, and any necessary safety measures. Despite the initial investment, many airports see significant long-term energy savings.
Which was the world’s first airport to become fully powered by solar energy?
Cochin International Airport in Kerala, India, became the world’s first fully solar-powered airport in 2015. This groundbreaking achievement set a new standard for sustainable airport operations globally. The airport’s solar initiative has since inspired many other aviation facilities to explore similar renewable energy solutions.
What are the visual characteristics of the solar power project at the Cochin International Airport?
The solar power project at Cochin International Airport features expansive arrays of solar panels. These panels are arranged in neat rows across 45 acres of unused land near the cargo complex. The installation includes both ground-mounted and rooftop panels, totalling over 46,000 solar modules. The panels have a matte finish to reduce glare and blend harmoniously with the airport’s landscape.
Is it feasible to install solar panels on airport grounds and what are the potential challenges?
Installing solar panels on airport grounds is indeed feasible, as demonstrated by numerous successful projects worldwide. However, you must navigate several challenges. These include ensuring panels don’t interfere with radar systems or create hazardous glare for pilots. Careful planning is necessary to avoid conflicts with future airport expansion plans. Wildlife management is another consideration, as solar arrays can attract birds, potentially increasing bird strike risks.
As of the latest figures, how many airports in India have adopted solar energy?
As of early 2025, over 50 airports in India have adopted solar energy to varying degrees. This figure represents a significant increase from previous years, reflecting India’s commitment to sustainable aviation practices. These solar initiatives range from small-scale rooftop installations to large ground-mounted arrays, collectively contributing to a substantial reduction in the aviation sector’s carbon footprint.