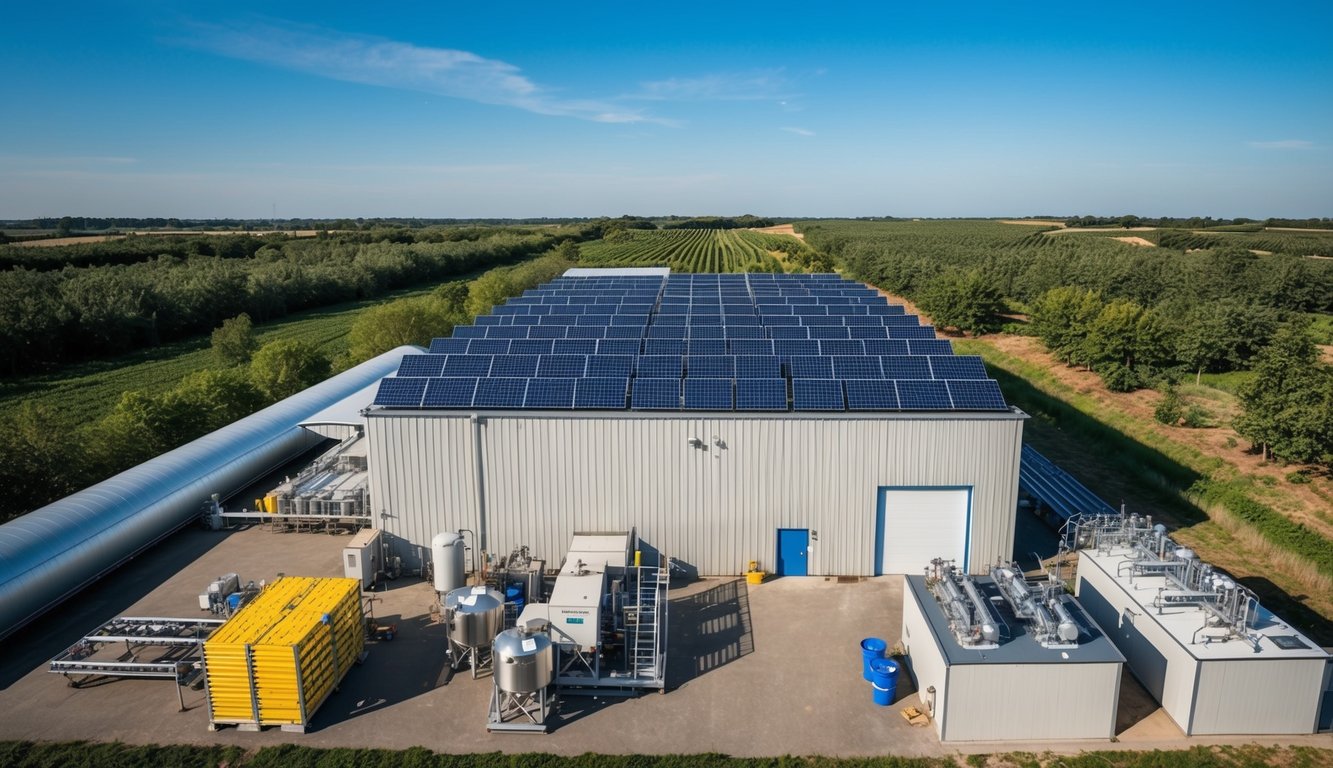
Solar Panels for Food & Drink Production: Powering Sustainable Culinary Industries
Solar panels offer food and drink producers a reliable source of clean energy, particularly beneficial for high-energy users. These systems can power temperature control systems and manufacturing processes, reducing reliance on traditional energy sources. Solar energy adoption in the food and drink sector not only demonstrates ecological responsibility but also provides a competitive edge in the market.
UK-based packaging companies have already embraced solar power to enhance their sustainability efforts and reduce emissions in production processes. This shift aligns with circular economy goals and helps meet corporate social responsibility objectives. The food and beverage industry’s move towards solar energy is driven by the need to reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
For businesses in this sector, solar panels offer substantial cost savings on energy expenditure. Companies can switch to low-cost, green solar energy without upfront costs through Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs). This approach allows food and drink manufacturers to invest in sustainable energy solutions whilst maintaining focus on their core operations.
Key Takeaways
- Solar panels provide clean energy for food and drink production, reducing operational costs and emissions
- UK packaging companies are adopting solar power to enhance sustainability and meet circular economy goals
- Power Purchase Agreements enable businesses to switch to solar energy without upfront costs

Understanding Solar Panels In Food Production
Solar panels are transforming energy usage in food and drink production. This technology offers significant benefits for processing plants, addressing high energy demands while promoting sustainability.
How Solar Energy Powers Food Processing
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, providing a clean power source for food processing facilities. These systems generate direct current (DC) electricity, which is then converted to alternating current (AC) for use in machinery and equipment.
Photovoltaic cells in the panels absorb solar radiation, creating an electric field that powers various food processing applications. Large solar arrays can be installed on rooftops or nearby land to meet the substantial energy needs of production lines, refrigeration units, and packaging systems.
Solar power systems can be integrated with existing electrical infrastructure, allowing facilities to seamlessly switch between solar and grid electricity as needed.
Benefits For Food Manufacturing Plants
Solar panels offer numerous advantages for food and drink producers:
- Cost savings: Reduced electricity bills
- Sustainability: Lower carbon emissions
- Energy independence: Less reliance on the grid
- Brand image: Enhanced eco-friendly reputation
Solar power systems provide a stable, long-term energy solution with minimal maintenance requirements. They can significantly reduce operational costs, especially for energy-intensive processes like heating, cooling, and drying.
By adopting solar energy, food manufacturers demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship, which can appeal to eco-conscious consumers and partners.
Energy Requirements In Food Production
Food and drink production is notably energy-intensive, with various processes demanding substantial power:
| Process | Energy Use |
|---|---|
| Heating | High |
| Cooling | High |
| Drying | High |
| Packaging | Medium |
| Cleaning | Medium |
Solar panels can effectively meet these energy needs, particularly during peak daylight hours when production is often at its highest. For processes requiring consistent power, hybrid systems combining solar with energy storage solutions can ensure uninterrupted operations.
Large-scale food processing plants may require extensive solar arrays to meet their energy demands. However, even partial adoption of solar power can lead to significant reductions in grid electricity consumption and associated costs.

Solar Panel Applications In Beverage Industry
Solar power systems are transforming drink production processes across various beverage sectors. These renewable energy solutions enhance sustainability and reduce operational costs for manufacturers.
Solar-Powered Brewing Systems
Breweries are embracing solar technology to power their operations. Photovoltaic arrays on brewery rooftops generate electricity for brewing equipment, bottling lines, and refrigeration units. This clean energy source helps brewers reduce their carbon footprint and energy bills simultaneously.
Many craft breweries have installed solar panels to cover a significant portion of their electricity needs. For example, some microbreweries use solar power for their mash tuns, kettles, and fermentation tanks. The steady daytime energy production aligns well with brewing schedules, allowing for efficient use of solar-generated electricity.
Solar thermal systems are also gaining traction in brewing. These systems heat water for the brewing process, further reducing reliance on conventional energy sources.
Winery Solar Solutions
Wineries are ideal candidates for solar power integration due to their rural locations and ample roof space. Solar installations at vineyards often power grape processing equipment, climate control systems for wine cellars, and bottling lines.
Some wineries have gone a step further by incorporating solar pumps for irrigation. These systems use solar energy to pump water from wells or reservoirs to the vineyards, reducing electricity consumption and associated costs.
Solar-powered electric vehicle charging stations are becoming common at wineries, allowing visitors to charge their cars while enjoying wine tastings. This added amenity enhances the winery’s eco-friendly image and attracts environmentally conscious customers.
Soft Drink Manufacturing Integration
Soft drink producers are leveraging solar energy to power their high-energy consumption processes. Large-scale solar arrays are being installed at bottling plants to offset electricity usage from the grid.
Solar power is particularly beneficial for running conveyor belts, filling machines, and packaging equipment. The consistent energy supply during daylight hours matches well with production schedules, maximising the use of solar-generated electricity.
Some soft drink manufacturers use solar thermal systems to heat water for cleaning and sterilisation processes. This application reduces the need for gas or electric boilers, further decreasing the facility’s carbon emissions.
Solar-powered refrigeration units are also gaining popularity in the soft drink industry. These systems help maintain optimal temperatures for ingredient storage and finished product cooling, ensuring quality whilst reducing energy costs.

Cost Benefits And ROI For Food Producers
Solar panels offer significant financial advantages for food and drink producers. They can substantially reduce energy costs and provide a solid return on investment over time.
Initial Investment Considerations
Food producers must carefully evaluate the upfront costs of solar panel installation. The price varies based on system size, panel quality, and installation complexity. A typical commercial system ranges from £50,000 to £500,000.
Key factors to consider:
• System size: Determined by energy needs and available space
• Panel quality: Higher efficiency panels cost more but yield better returns
• Installation: Rooftop vs ground-mounted systems affect costs
• Equipment: Inverters and batteries impact overall expenses
Despite the sizeable initial outlay, many food producers find solar panels a worthwhile long-term investment due to their potential for substantial energy savings.
Energy Cost Savings Analysis
Solar panels can dramatically lower electricity bills for food producers. The amount saved depends on factors such as system size, energy consumption, and local electricity rates.
A medium-sized food production facility might save £20,000 to £50,000 annually on energy costs. Over a 25-year lifespan, total savings could exceed £1 million.
Factors affecting savings:
• Energy usage: Higher consumption leads to greater savings
• Sunlight exposure: More sunshine equals more energy generation
• Electricity rates: Higher rates increase potential savings
• System efficiency: Better panels and maintenance maximise output
Food producers should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to estimate their specific savings potential.
Government Incentives For Food Industry
The UK government offers various incentives to encourage solar adoption in the food industry. These can significantly reduce installation costs and improve ROI.
Key incentives include:
- Business rates relief: Up to 100% relief on business rates for solar installations
- Capital allowances: Tax deductions for solar panel investments
- Smart Export Guarantee: Payments for excess energy exported to the grid
Some local authorities also provide grants or low-interest loans for renewable energy projects. Food producers should research available incentives in their area to maximise financial benefits.
By leveraging these incentives, food producers can shorten the payback period for their solar investment, often to less than 5 years.

Implementation Strategies And Best Practices
Implementing solar panels in food and drink production facilities requires careful planning and adherence to specific guidelines. Proper installation, maintenance, and compliance with food safety standards are crucial for successful integration.
Installation Requirements For Food Facilities
Solar panel installation in food facilities demands unique considerations. Panels must be placed strategically to avoid interference with production processes and maintain hygienic conditions.
Roof integrity is paramount. A structural assessment ensures the roof can support the additional weight of solar panels.
Waterproofing measures are essential to prevent moisture ingress, which could compromise food safety.
Wiring and inverters should be installed in separate, sealed areas to prevent contamination. Use food-grade materials for any components near production zones.
Consider shadow-free zones to maximise energy generation. This may involve repositioning equipment or using specialised panel layouts.
Incorporate monitoring systems to track energy production and detect any issues promptly.
Maintenance In Food-Safe Environments
Regular maintenance is vital for optimal performance and food safety compliance. Develop a cleaning schedule that aligns with facility hygiene protocols.
Use food-safe cleaning agents approved for solar panel maintenance. Avoid harsh chemicals that could potentially contaminate production areas.
Pest control measures should be implemented around solar installations to prevent infestations.
Schedule inspections during non-production hours to minimise disruption and contamination risks.
Train maintenance staff on food safety protocols specific to working in production environments.
Implement a record-keeping system for all maintenance activities, ensuring traceability and compliance with food safety audits.
Compliance With Food Safety Standards
Integrating solar panels must not compromise food safety standards. Consult with food safety experts during the planning phase to ensure compliance.
Conduct a hazard analysis to identify potential risks associated with solar panel installation and operation.
Update your HACCP plan to include solar panel-related critical control points.
Ensure all materials used in the solar installation are food-grade certified where necessary.
Implement microbial testing protocols for areas around solar installations to monitor for potential contamination.
Document all processes related to solar panel operation and maintenance in your food safety management system.
Regular audits should include solar panel systems as part of the overall food safety assessment.

Real-World Success Stories
Solar panels are revolutionising food and drink production, offering significant cost savings and environmental benefits. Companies of all sizes are embracing this technology to power their operations sustainably.
Major Food Manufacturers Using Solar
Dawn Foods, a leading bakery manufacturer, has integrated solar energy into its sustainability strategy. The company supplies products to high street bakeries, supermarkets, and food service companies. By adopting solar power, Dawn Foods has made strides in reducing its carbon footprint, aligning with its century-old commitment to innovation.
Alara Wholefoods stands out as a pioneer in eco-friendly food production. This UK-based company was the first food manufacturer to achieve zero waste status. Alara’s dedication to sustainability extends to its energy usage, with solar panels powering its production facilities. This approach has helped Alara maintain its position as an industry leader in organic and gluten-free cereals.
Small-Scale Production Examples
Small-scale producers are also reaping the benefits of solar energy. The Johnson family, featured in a case study, installed solar panels on their property to power their artisanal food production. This move allowed them to:
- Reduce electricity costs by 70%
- Increase production capacity without raising overheads
- Enhance brand image as an eco-conscious producer
Local breweries and dairy farms have similarly adopted solar technology, using roof-mounted panels to power refrigeration units and processing equipment.
Sustainability Achievements
Food and beverage manufacturers using solar panels have reported impressive sustainability gains. A study of 50 companies revealed:
| Achievement | Average Improvement |
|---|---|
| Carbon emissions reduction | 40% |
| Energy cost savings | 30% |
| Brand value increase | 15% |
These figures demonstrate the tangible benefits of solar adoption in the food sector. Distribution centres have seen particular success, with large roof areas ideal for expansive solar arrays. Some facilities now generate excess power, feeding clean energy back into the grid.
Warehousing facilities have also benefited, using solar power for climate control and automated systems. This approach has led to more stable temperatures for food storage and reduced spoilage rates.

Environmental Impact And Sustainability
Solar panels in food and drink production significantly reduce environmental harm whilst promoting sustainable practices. They offer a clean energy solution that aligns with eco-friendly manufacturing goals.
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Solar panels substantially decrease carbon emissions in food and drink production. By harnessing sunlight, these systems generate electricity without burning fossil fuels. This clean energy source replaces traditional power methods, cutting greenhouse gas output.
Food manufacturers can lower their carbon footprint by up to 70% with solar adoption. Large-scale solar installations on factory roofs or nearby land provide ample power for production lines, cooling systems, and other energy-intensive processes.
Energy independence also reduces reliance on grid electricity, often derived from non-renewable sources. This shift supports national and global climate targets, helping the food industry contribute to a greener future.
Waste Management Integration
Solar power complements waste management efforts in food production. Excess energy generated can power waste treatment facilities, creating a closed-loop system.
Solar-powered composting units transform food scraps into nutrient-rich soil amendments. This process reduces landfill waste and creates valuable resources for sustainable farming practices.
Anaerobic digesters fuelled by solar energy convert organic waste into biogas, providing an additional energy source. This integration maximises resource efficiency and minimises environmental impact.
Solar-powered water treatment systems purify wastewater, allowing its reuse in non-food applications like cleaning or irrigation. This approach conserves water and reduces the strain on local water supplies.
Sustainable Food Production Goals
Solar energy supports broader sustainable food production objectives. It enables manufacturers to meet stringent environmental standards and consumer demands for eco-friendly products.
Energy cost savings from solar allow reinvestment in other sustainable initiatives, such as:
- Biodegradable packaging materials
- Water-efficient processing equipment
- Local ingredient sourcing to reduce transport emissions
Solar adoption often sparks a culture of sustainability within organisations. This mindset shift leads to innovation in product design, manufacturing processes, and supply chain management.
Companies leveraging solar power enhance their reputation as responsible corporate citizens. This positive image can boost brand loyalty and attract environmentally conscious consumers, driving long-term business growth.

Future Trends and Innovations
Solar technology for food and drink production is rapidly evolving. New developments are transforming energy efficiency and sustainability in the industry.
Emerging Solar Technologies
Perovskite solar cells represent a promising advancement. These cells offer higher efficiency and lower production costs compared to traditional silicon panels. Thin-film solar technologies are also gaining traction, providing flexible and lightweight options for diverse installation needs.
Bifacial solar panels are becoming increasingly popular. These panels capture sunlight from both sides, boosting energy yield by up to 30%. This technology is particularly beneficial for ground-mounted systems in food production facilities.
Concentrated solar power (CSP) systems are being refined for industrial applications. CSP uses mirrors to focus sunlight, generating high temperatures for food processing and sterilisation.
Smart Energy Management Systems
Artificial intelligence is revolutionising solar energy management. AI algorithms optimise energy distribution, predicting consumption patterns and adjusting output accordingly. This leads to more efficient use of solar power in food production facilities.
Internet of Things (IoT) devices are enhancing monitoring capabilities. Sensors throughout the production line provide real-time data on energy consumption, allowing for precise adjustments and reduced waste.
Blockchain technology is being integrated into energy management systems. This improves transparency and security in energy transactions, particularly beneficial for facilities with excess solar power to sell back to the grid.
Industry Growth Projections
The solar market in food and drink production is expected to grow significantly. Analysts predict a compound annual growth rate of 12% from 2025 to 2030.
Government incentives and regulations are driving adoption. Many countries are offering tax breaks and grants for solar installations in industrial settings.
| Year | Projected Market Value (£ Billion) |
|---|---|
| 2025 | 3.2 |
| 2027 | 4.0 |
| 2030 | 5.6 |
Falling costs of solar technology are making installations more accessible. Prices are projected to decrease by 15% annually, further accelerating industry-wide adoption.
Conclusion
Solar panels offer significant advantages for food and drink producers. You can reduce energy costs and enhance sustainability by harnessing the sun’s power. Many companies in the sector have already adopted this technology with positive results.
The benefits extend beyond financial savings. Solar energy helps decrease carbon emissions, aligning your operations with environmental goals. This can boost your brand image and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
While initial installation costs may seem high, long-term savings often outweigh the investment. Government incentives and falling panel prices make solar increasingly accessible.
Consider these key points:
• Energy efficiency: Solar panels can offset a substantial portion of your electricity usage
• Sustainability: Reduced reliance on fossil fuels lowers your carbon footprint
• Cost savings: Lower energy bills improve profitability over time
• Brand value: Demonstrating environmental responsibility can attract customers
As the food and drink industry faces pressure to reduce emissions, solar power presents a viable solution. By embracing this clean energy source, you position your business for a more sustainable and profitable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solar panels for food and drink production offer numerous benefits but also raise important questions. Let’s address some common queries about costs, equipment, applications, and industry guidance.
What are the costs associated with installing solar panels for food and drink production facilities?
The costs of installing solar panels for food and drink production facilities vary widely depending on factors such as system size, location, and specific energy requirements. Initial investment typically ranges from £50,000 to £500,000 for commercial-scale installations. However, many businesses recoup these costs within 5-10 years through reduced energy bills and government incentives.
Which solar panel brands are recommended for powering food and beverage production?
Several reputable brands are well-suited for food and beverage production environments. SunPower, LG, and Panasonic are known for their high-efficiency panels that perform well in industrial settings. REC and Canadian Solar offer durable options that withstand harsh conditions often present in food processing facilities.
How can solar panels be utilised to produce drinking water?
Solar panels can power desalination and purification systems to produce drinking water. These systems use reverse osmosis or distillation processes, which require significant energy input. Solar-powered units can operate in remote locations or supplement grid power in large-scale water treatment plants.
How can one calculate the number of solar panels required for culinary applications?
To calculate the number of solar panels needed for culinary applications, assess your daily energy consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Divide this by the average daily sun hours in your area and the wattage of your chosen solar panels. This gives you an estimate of the panel quantity required to meet your energy needs.
What is the estimated solar power capacity needed to operate a mobile food truck?
A typical mobile food truck requires approximately 3-5 kW of solar power capacity to operate essential equipment like refrigerators, cooking appliances, and lighting. This translates to roughly 10-15 solar panels, depending on their efficiency and the specific energy demands of your mobile kitchen.
Have any consumer advocates provided guidance or reviews on the use of solar panels in the food industry?
Consumer advocates have highlighted the positive impact of solar panels in the food industry, focusing on sustainability and cost-effectiveness. Which? and the Energy Saving Trust provide impartial advice on solar panel selection and installation for businesses. They emphasise the importance of proper sizing, quality equipment, and reputable installers to maximise benefits for food and drink producers.